SimSpin is an R package designed to transform a galaxy simulation into a "mock" integral field spectroscopy (IFS) observation, originally written as a part of the PhD Thesis “From Particles to Pixels: Using numerical simulations to investigate observable galaxy kinematics” by Dr. Kate Harborne (2020). The package facilitates the development of simulations by directly highlighting the impact that tuning physical parameters has on observables. SimSpin has played an important role in a number of research publications, including in the Middle Ages Galaxy Properties with Integral Field Spectroscopy (MAGPI) Theory Data Release where SimSpin helps by producing mock observations of HETDEX Pilot Survey (HPS) to mimic the MAGPI observations. MAGPI is a large programme on the European Southern Observatory Very Large Telescope, using new medium-deep adaptive optics aided Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) observations of fields selected from the Galaxy and Mass Assembly (GAMA) survey.
Dr. Harborne came to ADACS in 2022 proposing the development of a web application for the existing SimSpin code. The aim was to build a web-based Application Programming Interface (API) and Graphical User Interface (GUI) that allow users to interact with the code visually and intuitively. The previous prototype application used R-Shiny framework, which suffered from limited support for file transfers, API and asynchronous mode.
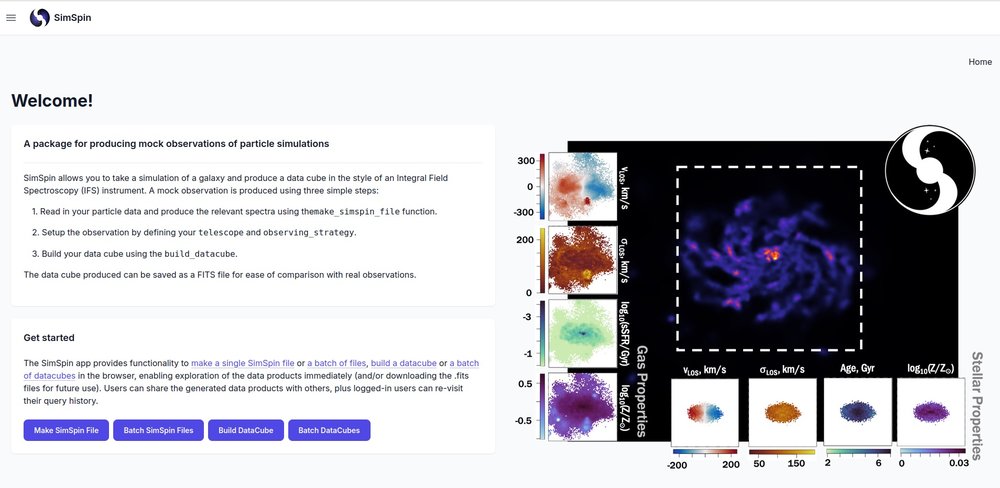
Through ADACS, an interactive web-based app for visualising galaxy simulations in the browser using the SimSpin R package was developed, enabling the dynamic exploration and visualisation of theoretical galaxies (and/or downloading .FITS files for offline use), underpinned by a robust well-documented RESTful API web service for programmatic access. The app is asynchronous (the user can be notified when their request is complete), and allows for instant data exploration via a dedicated viewer, with multiple colour maps and image scaling functionality right in the browser. The FITS header is available and users are able to load multiple file extensions into the viewer. The web app and RESTful API are served on Data Central infrastructure, which provides both the hosting and storage requirements.
On an Australian Research Data Commons (ARDC) interview upon winning the 2024 ARDC-sponsored Emerging Leaders in Astronomy Software Development Prize by the Astronomical Society of Australia for developing SimSpin, Dr. Harborne shared, “Thanks to Liz Davies, Simon O’Toole and others, a beautiful web app was created around an API that allows users to interact with the code visually and intuitively. This web app has dramatically increased the use of SimSpin around the world, with users coming from Germany, the US and the UK as well as Australia. Through this collaboration, we’re hoping to provide similarly consistent and comparable mock observations of galaxies from more simulations.”
This initial project has since expanded to several new initiatives, creating opportunities for Macquarie and Swinburne nodes to collaborate and leverage their combined expertise. In 2023B and 2024B semesters, a GUI for the existing batch mode was developed for the SimSpin web app. The new GUI streamlines the batched operations, making it easier for users to run a single simulation cutout at a number of different inclination angles and observe a simulated galaxy with various telescopes.

Check out some of our other projects.
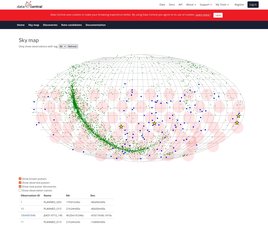
ADACS developed a web-based database and interface for the SMART pulsar survey, enabling cone searches, candidate ranking, and editing. The upgrades led to new pulsar discoveries, with data to be made publicly accessible via Data Central.
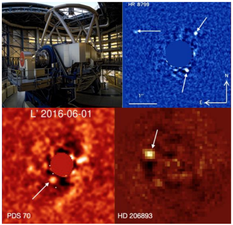
ADACS significantly enhanced the NaCo pipeline by parallelising key functions within the VIP library, reducing execution times by a factor of six and enabling more efficient processing of direct imaging data from the ESO archive and beyond.
ADACS developed the "eso-downloader" Python package to automate ESO telescope data downloads. It streamlines access, quality checks, and retrieval, improving efficiency for astronomers in large programmes like GECKOS and MAUVE.